A stored procedure is group
of Transact SQL statements. If you write
a same query again and again then we can write that query as Stored procedure and
call it by its name.
Here we will learn Stored procedure in EF with an example.
Step(1): First create a table with name “StudentStoredProcedure” and give column name for this table and
insert some value to this.
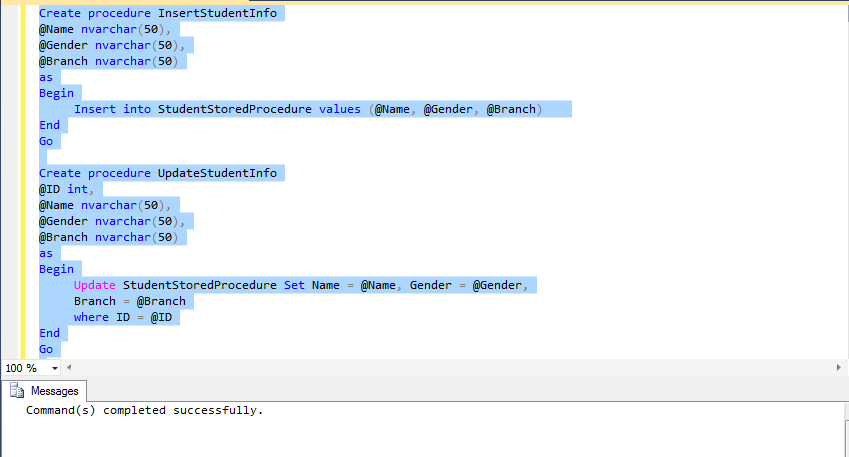
Step(2): Now create stored procedure for insert
update and delete.
Create procedure InsertStudentInfo
@Name nvarchar(50),
@Gender nvarchar(50),
@Branch nvarchar(50)
as
Begin
Insert
into StudentStoredProcedure values (@Name, @Gender, @Branch)
End
Go
Create procedure UpdateStudentInfo
@ID int,
@Name nvarchar(50),
@Gender nvarchar(50),
@Branch nvarchar(50)
as
Begin
Update
StudentStoredProcedure Set Name = @Name, Gender = @Gender,
Branch = @Branch
where
ID = @ID
End
Go
Create procedure DeleteStudentInfo
@ID int
as
Begin
Delete
from StudentStoredProcedure where ID = @ID
End
Go
|
After
writing this stored procedure script execute this and go to Programmability and
expand stored procedure there you will 3 store procedure with name “InsertStudentInfo”, “UpdateStudentInfo” , “DeleteStudentInfo”
Step(3): Now Create a new project and Right click on solution
explorer and click on “add new item” and select “Ado.net entity data modal” and
select "EF Designer from database". And click on next
Step(3): Here give the
connection and select your table and specify the app.config name as “SP_EntityFramework”.
And click on next
Step(3): Select table name as StudentStoredProcedure. First check that Import selected stored procedures and
functions into the entity model checkbox is selected or not and then
click Finish.
Step(4): After click on finish your entity data
modal is create and stored procedure as well but here you will not be able to
see stored procedure.
To view stored procedure.
1.
Go to the entity model designer surface and click on "Model Broswer" .
2. Now Expand Stored Procedures folder and you will see your stored
procedures.
Step(5): Go the Mapping Details, here you will see <Select Insert Function>, <Select Update Function>, <Select Delete Function>. Select one stored procedure for each one eg.
Step(6): select for InsertStudent info and as
like that you can set for all the functions.
Step(7): Now, we have to validate it before executing for ensure
that it will give error or not. Right click on designer surfer and click on validate.
Step(8): Add a form and Dreg and down a datagrid view from tool box.
Go to “smart tag of datagrid view and add
columns to this. When you will click on “add column” link you will see this
screen.
After adding column click OK. After then the Datagridview
will be like this.
Step(9): Again go to “smart tag of Datagrid view
and select DataSource as “BindingdataSource1”. In this screen you will see a
link as “Add project dataSource” ,
click on this,
Add project dataSource -> Database ->
Dataset - > Give connection -> Give connection string name
After click on next you will see your tables
select table and select your stored procedure after when you will click on OK
button your Datagridview. When you will run application at this time you will
see data in datagrid view.
And this code will generate automatically.
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// TODO: This line of code loads data
into the 'for_entityDataSet.StudentStoredProcedure' table. You can use, or
remove it, as needed.
this.studentStoredProcedureTableAdapter.Fill(this.for_entityDataSet.StudentStoredProcedure);
}
|
Double click on DataGrid view and
write code for “Delele” and “insert”
And give the connection also
builder.DataSource
= "MUNESH ";
builder.InitialCatalog = "ForEntity";
builder.IntegratedSecurity = true;
|
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// TODO: This line of code
loads data into the 'for_entityDataSet.StudentStoredProcedure' table. this.studentStoredProcedureTableAdapter.Fill(this.for_entityDataSet.StudentStoredProcedure);
}
private void
dataGridView1_CellContentClick(object sender, DataGridViewCellEventArgs e)
{
//delete the row form
database on gridview buttion click
if (e.ColumnIndex ==
1)
{
using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(builder.ToString()))
{
using (SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("Ten Most
Expensive Products", conn))
{
try
{
conn.Open();
cmd.CommandType =
CommandType.StoredProcedure;
// _customQuery = new CustomQuery();
// SqlCommand
sqlcmd= new SqlCommand();
SqlParameter parm= null;
cmd.CommandText =
"DeleteStudentInfo" ;
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@ID", Convert.ToInt64(dataGridView1.Rows[e.RowIndex].Cells[2].Value));
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
conn.Close();
Form1_Load(sender, e);
}
catch
{
}
}
}
}
//INSERT into the row form
database on gridview buttion click
if (e.ColumnIndex ==
0)
{
using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(builder.ToString()))
{
using (SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("Ten Most
Expensive Products", conn))
{
try
{
conn.Open();
cmd.CommandType =
CommandType.StoredProcedure;
// _customQuery =
new CustomQuery();
// SqlCommand
sqlcmd= new SqlCommand();
SqlParameter parm= null;
cmd.CommandText =
"InsertStudentInfo";
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name", "MUNESH");
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@GENDER", "MALE");
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@BRANCH", "IT")
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
conn.Close();
Form1_Load(sender, e);
}
catch
{
}
}
}
}
}
|
Step(10): Now run your application you will get
the output.